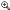SAP has succeeded in moving towards a modern coherent planning suite with the release of SAP BPC 10.1, version for SAP NetWeaver. The new product combines the advantages of BW Integrated Planning, SAP HANA and SAP BPC.
SAP BPC 10.1 NetWeaver version offers a Standard as well as a new Embedded model. While the Standard Model does not differ much from the BPC 10.0 for NetWeaver, the Embedded model provides a planning suite that is based technologically on SAP BW 7.4/7.5 on HANA and combines the planning components of SAP BW Integrated Planning and SAP BPC.
In this insight, you will find a high level technical overview of SAP BPC and its basic architecture components. The focus is on BPC Embedded, its advantages, weaknesses and differences with the BPC Standard.
At the same time, we address a number of typical questions people ask about SAP BPC nowadays:
- What are the different versions of SAP BPC available?
- What is new in BPC embedded on HANA?
- What is the difference between BPC and BW IP?
- What is IBP (Integrated Business Planning) and its role?
- What are the pros and cons for different SAP Business Planning and Consolidation tools in relation to the latest releases of SAP HANA, Netweaver, S/4HANA and BPC?
Available BPC Versions
Today there are about 5 different versions of SAP BPC available from SAP depending on how you count:
- SAP BPC 10.1 Microsoft,
- SAP BPC 10.1 NetWeaver Standard on traditional database (e.g. Oracle, db2),
- SAP BPC 10.1 NetWeaver Standard on HANA,
- SAP BPC 10.1 Embedded on HANA, and
- SAP BPC Optimized for S/4 HANA.
This may sound confusing and overwhelming. We will focus below on the SAP BPC Embedded version and go through its specific features, advantages and weaknesses.
What is New in BPC Embedded vs. Standard?
BPC Embedded (or in other words BPC Unified [old term]) is one single platform for Planning, Consolidation and Reporting leveraging the power of SAP HANA on large datasets together with the flexibility and appeal of SAP BPC front-end modelling capabilities to business users (LOB). On the other hand SAP BPC Embedded leverages the powerful BW on HANA data warehousing capabilities and modern Business Objects tools for reporting, dashboards and apps.
Figure 1: BPC Embedded, One platform for Reporting, Planning, Consolidation
A bulk of BPC Embedded modelling is performed using the BW and BI IP engine as opposed to BPC Standard, where a web based administration console is used as a frontend.
Therefore, IT involvement in BPC Embedded modelling is crucial. Modelling objects for each product are shown in the high level chart below. BPC standard also uses an EPM add-in for reporting/Excel based data entry while BPC embedded uses Analysis for Office.
To write data to the system, with BPC Standard the end-user can create an input form with the EPM add-in. To do this in BPC embedded, the user needs to first create an input enabled query (in BEx query designer or Eclipse/HANA Studio) and an Analysis for Office workbook.
Figure 2: Modelling in BPC Embedded vs. BPC Standard
In BW 7.5 on HANA, modelling in BPC Embedded can be based on ADSO objects (Planning, Direct Update) instead of InfoCubes/Multiproviders/DSO’s.
Using Direct Update ADSOs instead of InfoCubes simplifies architecture and makes modelling a straight forward process as all relevant infoobjects can be collected in the ADSO and data slices can be defined in the aggregation levels.
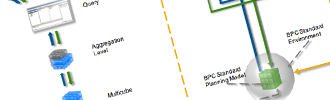
High level BPC Embedded components and tools involved in modelling together with user frontend tools are described in the following chart.
Figure 3: BPC Embedded components in BW 7.5 on HANA
Modeling Approach
|
SAP BPC Standard |
SAP BPC Embedded |
|
|
Dimensions |
Account based model with the following mandatory dimensions:
|
Key Figure based model with the following Characteristics:
|
|
Values |
Measure: only one technical key figure in BPC generated BW InfoCube |
Key Figures, of various types:
|
|
Hierarchies |
BPC hierarchies, correspond to BW hierarchies with postable nodes |
BW hierarchies with different node types; also display hierarchies in BW queries |
|
Modelling Slices |
Each planning slice has to be modelled separately as a separate model |
Slices can be created on top of a single InfoCude (ADSO) as aggregation levels |
|
Data transfers |
You may need to copy data between models, e.g. HR numbers to be copied to the P&L model |
No need to copy data between models as different slices can be set up on top of the same dataset with automatic disaggregation |
|
Copying Actuals |
The planning model has to contain actuals copied from the actuals dataset |
The planning model contains only forecasted/plan figures. The actuals are read from the actuals dataset |
The fundamental difference in modelling is that SAP BPC Embedded requires data modelling in BW/IP, while BPC Standard modelling is done by business users in the BPC frontend.
Data Validation Rules
|
BPC Standard |
BPC Embedded |
|
|
Constraints for persistence |
BPC Rules; validations can also be implemented using Script Logic. BADI can be used as well. |
Characteristic Relationships (methods CHECK, DERIVE, CREATE); validations can also be implemented using FOX or exit planning functions
|
|
Data protection |
BPC Work Status |
Data Slices, BPC Work Status (mapped to technical data slices at run time) |
Advantages of SAP BPC Embedded related to the platform (BW on HANA)
- SAP’s strategic EDW platform
- Reduction in data size
- Improved performance (both data loading and query execution)
- Big Data platform
- Predictive Analytics capabilities
- Integration with SAP BusinessObjects reporting tools (especially BO Design Studio and BO Analysis for MS Office)
Advantages of SAP BPC Embedded vs. Standard
- No need to replicate data and/or models between BW and BPC
- Less models will be needed as aggregation levels will be used.
- Many standard planning functions available (copy, disaggregation, formula…)
- Calculations pushed to HANA (including disaggregation) allowing very fast responsive times on large datasets. With BPC Standard, many calculations are still running the ABAP stack/application layer.
- Access to powerful data logic transformations with SQLScript and ABAP
- Virtual modelling capabilities (adding remote data sources)
- Integration with SAP BusinessObjects reporting tools (especially BO Design Studio and BO Analysis for MS Office)
Weaknesses of SAP BPC Embedded vs. Standard
- BPC Embedded models cannot be owned purely by LOB, modelling requires more involvement of IT as data models are based on objects in BW, IP and BEx queries. It can be configured in a way that it is maintained by LOB at a later stage, but the initial setup requires involvement of IT/consultants.
- Consolidation module in BPC Embedded is quite new, not proven on the market yet.
Conclusion
BPC Embedded combines the benefits of SAP BPC Standard, BW IP and SAP HANA, which makes this a unique Planning and Consolidation solution that is expected to bring a lot of value to its customers.
A SAP BPC Planning and Consolidation user interface for the business, combined with complex planning functions and disaggregation scenarios native in HANA on large datasets makes this a very powerful & fast solution to definitely take into consideration for new planning & consolidation projects.
Some Terminology
|