ISK Biosciences Europe brings several new agricultural products to serve a growing global market. These agricultural products can be roughly divided in 3 product categories:
- Fungicides – Control of diseases on potato, fruit/vegetables, cereals etc.
- Herbicides – for weed control;
- Insecticides – Control of the feeding of sucking insects.
The company ISK Biosciences Europe is positioned to respond to promising new opportunities and is developing products discovered by the parent company Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha (ISK) Ltd. in Japan.
ISK Biosciences Europe manufactures their products across several plants at different locations. A limited number of distributors, located all over the world are responsible for supplying the products.
The Sales estimates (budget and forecast) and the Operational planning for the manufacturing plants are centrally managed at the administrative office ISK Bioscience Europe, located in Brussels (BE). The process of Sales & Operational Planning (S&OP) within ISK Biosciences is fully supported by a Planning Analytics TM1 web application.
Sales Planning
The Planning process is a joint effort with shared responsibility across the Marketing department, Sales department and Production department.
The Planning process consists of the yearly budget and a monthly forecast activity. The end-result of the yearly budget process is a detailed estimate of the volumes, prices and sales amounts. The forecast is a monthly update (refinement) of the original approved budget.
The Planning process itself is designed and implemented within an IBM Planning Analytics TM1 Web Application in such a way that:
- The efforts for data entry, by the sales responsible, is limited to a minimum;
- All metadata (dimensional data) and other relevant data is automatically uploaded via scheduled processes from the ERP-Source system. This automation avoids human mistakes and reduces the redundancy of the administrative burden;
- The process can be driven and structured by updating parameters, thus offering the administrator a maximum of flexibility and minimizing the workload of future development;
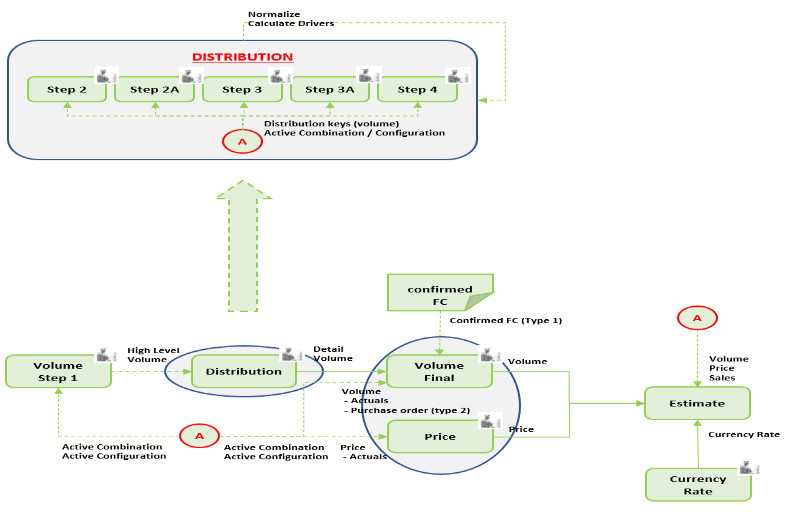
The yearly budget process uses a "phased waterfall" principle to distribute the high-level budgeted volumes per Product Group (4 digits) to the lowest level, the Unique Product Codes (13 digits). This waterfall process consists of the following successive phases:
- Phase 1: High level data entry on Customer Group, Product Group and Year
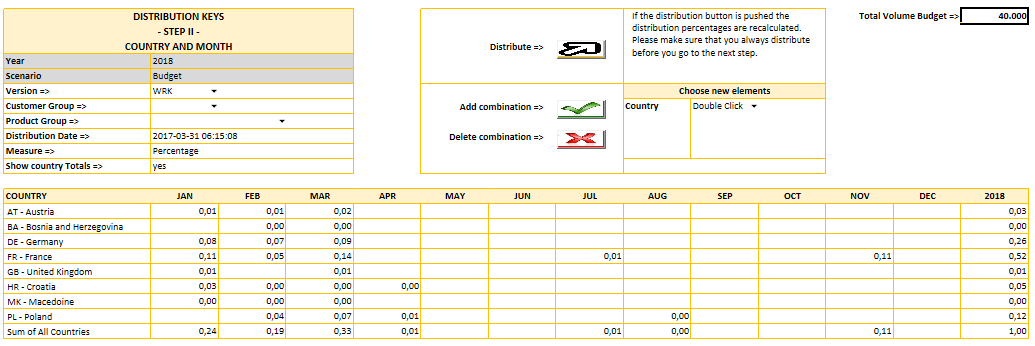
- Phase 2: Distribution to Country and Month;
- Phase 2A: Distribution to Trademark;
- Phase 3: Distribution to Packaging Size;
- Phase 3A: Distribution to Customer;
- Phase 4: Distribution to Manufacturing plant;
- Phase 5: Possibility for multi-level adjustment of detailed and/or aggregated distributed volumes by using standard TM1 spreading functionality;
Historical sales data are used to generate the distribution keys. At each phase of the waterfall process, the person in charge of the sales planning can adjust, delete or add new distribution keys.
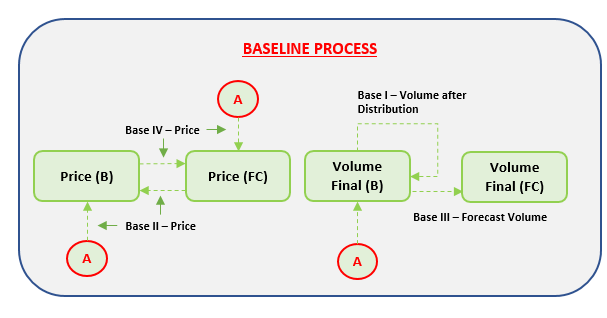
For estimation of the (sales) prices there are 2 scenarios at hand:
- Clean Sheet – (Sales) Prices can be entered from scratch without using a baseline scenario;
- Using a Baseline scenario – Within the baseline scenario, a choice is available between:
o What scenario is to be used as the baseline (source) for the budget prices (actuals, forecast, another version of budget)
o What is the percentage of price change
The volumes together with the prices make up the Sales Budget. The yearly budget dataset serves as the baseline (starting point) for the first forecast exercise.
The forecast is a monthly recurring exercise that consists of:
- Monthly growing actuals - data is retrieved via daily scheduled uploads from the ERP Source system
- Confirmed Forecast - (Sales Order) data is retrieved via daily scheduled uploads from the ERP Source system
- (Non-Confirmed) Forecast – data is manually updated by the sales representative in the application
Both the budget and forecast process allow to handle versions, this allows storing final and/or intermediate versions of the Sales Planning exercise. The main objective of this version management functionality is:
- Facilitate the analysis of the impact of different scenarios of sales data;
- Facilitate the analysis of the effectiveness and correctness of the sales planning process;
The sales process is designed in such a way that it can be steered by defining specific parameters. As such, the planning process is more flexible and future proof avoiding the necessity of frequent design changes. An example of such parameter is the possibility of setting out the number of years of actual data as a horizon for determining the distribution keys within the different budget steps. The setting for these parameters are centrally managed by the Sales Administrator Role.
Operational Planning
The main objectives of the operational planning for the manufacturing plants is to ensure that:
- The production quantities do not exceed the production capacity of the plants
- Just-In-Time delivery of materials to the production plants
- Up-to-date, real-time communication of production figures with all the planning stakeholders
- Early-warning insight of the impact of the changing demand of end-products or other variables
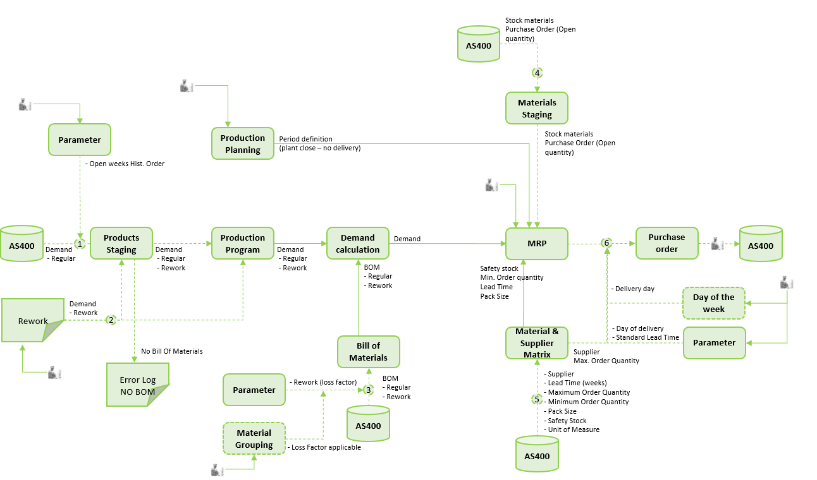
The operational planning consists of the following modules:
- Production Planning
- Production Program
- Demand Calculation
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
- Creation of Purchase Orders
As for Sales Planning the application for Operational Planning is designed in such a way to assure that:
- The effort for data entry by the operational planner is kept to a minimum
- All metadata (dimensional data) and other relevant data is automatically uploaded via scheduled processes from the ERP-Source system. This automation avoids human mistakes and reduces the redundancy of the administrative burden
- The process can be driven and structured by updating parameters, so to offer the administrator a maximum of flexibility and minimize the workload of future development
Production Planning
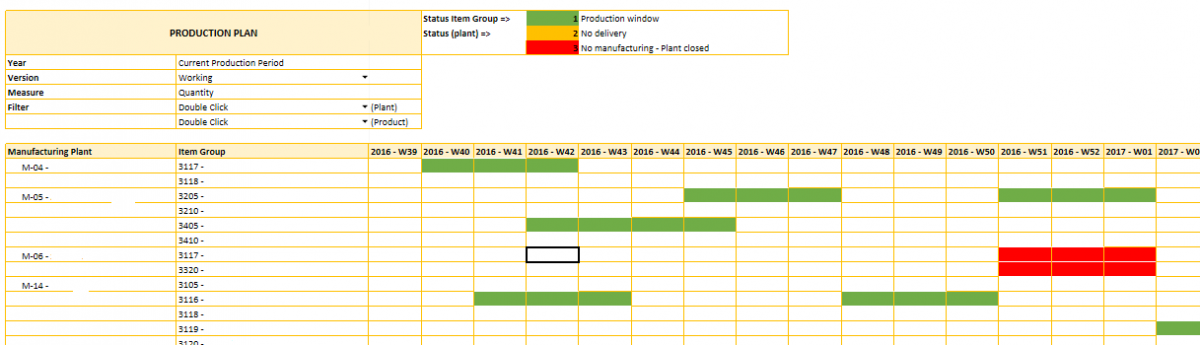
The production planning is a global master planning schedule for a manufacturing plant, in which the production windows of the different product groups are scheduled. In this module, the time allocated for “Plant Closure” and “No delivery periods” are planned as well. The production planning serves as input for the MRP-Planning.
Production program
The production program is a detailed scheduling of production volumes per individual end-product and per day. The data driving this process (confirmed sales orders) is retrieved via daily scheduled uploads from the ERP Source system. If required, the data can be manually adjusted by the planner for:
- Rework – negative demand for end-products (Material Recovery)
- Additional demand of finished-products
The production program and the production planning serves as the basis for the operational meetings between the operational responsible employees of the different manufacturing plants.
Demand Calculation
The module for the demand calculation forms the core calculation engine of the operational planning process. Based on the Bill of Material (BOM) for each of the (semi)finished-products the demand for materials is calculated via the BOM-explosion functionality. The module for demand calculation is the balancing act between the demand for end-products and the need for supply of base materials. The demand calculation is a real-time functionality that calculates the demand for the materials for the manufacturing plants, on the fly.
Materials Requirements Planning
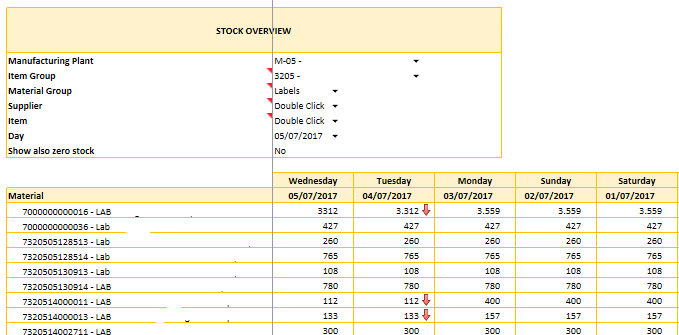
In the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) the demand for materials is converted into Purchase Order (PO) volumes for a (Default) supplier, taking into account:
- Historical, Current and Predicted Stock
- Unit of Measure
- Lead Time (in weeks)
- Minimum Order Quantity
- Pack Size
- Maximum Order Quantity
- Safety Stock
- Default Supplier
- Plant closure / no delivery possible (=> Production Planning)
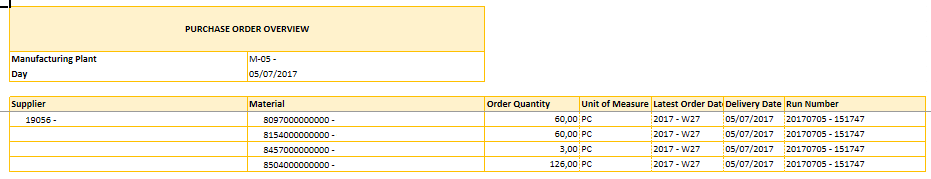
Creation of purchase orders
The last step in the operational planning is the creation of purchase orders for the material delivery. This process creates a purchase order suggestion that can be uploaded towards the ERP-Source system.
The operational planning is designed as such to allow optimisation, by tweeking the parameters at hand of the application administrator(s). These parameters determine the behaviour of the operational planning. Examples of these parameters are:
- Percentage Loss Factor Rework
- Standard Day of Delivery
- Current Week
- Standard Lead Time (weeks) – when no available
- Open weeks Historical order
The operational planning application facilitates version management, allowing for storing final and intermediate versions of the operational planning exercise. The main objective of this version management functionality is:
- Facilitate the analysis of the impact of different scenarios on the operational planning
- Facilitate the analysis of the effectiveness and correctness of the operational planning process
Summary
At ISK Biosciences, both the Sales planning as well as the Operational planning are highly optimized within an IBM Planning Analytics TM1 web application. The application offers a great deal of flexibility and automation to support the planning personnel through their workload, offering them tools at hand that target to decrease the time spent on composing the plan in favor of the time available for analyzing and finetuning the planning outcome.