Tim Hermie

Many organizations struggle with the lack of a correct 360° customer view. The same customer often appears multiple times across databases due to spelling variations, inconsistent formatting, or the creation of new profiles without checking for existing ones. Over time, this leads to poor data quality and operational issues.
Duplicate customer records pollute the data:
Transaction history is spread across multiple profiles
Marketing campaigns target the same customer more than once
Customer insights and analytics become biased
Manual data cleaning takes significant time and effort
This not only frustrates internal teams but also results in a poor experience for customers.
Customer deduplication addresses this by defining what makes a customer unique and enforcing it consistently.
The result is a clean customer table where duplicates are merged under a single customer ID and customer details are aligned across all related records.

Customer deduplication is implemented through a clear, repeatable pipeline, tailored to the client’s data and business rules:
Data normalization
Input attributes are cleaned and standardized. This includes actions such as standardizing street names, formatting names consistently, and validating values like age ranges or postal codes.
Hard matching
Strict matching rules are applied to identify exact duplicates, for example based on identical email addresses, customer numbers, or fully matching personal details.
Soft matching
Similarity-based comparisons are used to detect likely duplicates that are not exact matches. Configurable thresholds help identify records that are probably the same customer despite small differences or spelling errors.
Data alignment
Once records are linked, customer attributes are merged or prioritized according to predefined rules, ensuring consistent and reliable master data.
The deduplication process at one of our fashion retail customers runs as an automated workflow, optimized for project-specific requirements and scheduled to run daily. It continuously detects new master customer combinations by processing:
Updates to existing customer records
Newly ingested customer data
By leveraging the scalable compute and storage capabilities of Microsoft Azure and Databricks, the solution handles large volumes of customer data efficiently while remaining flexible as data grows.
The outcome is a trusted, up-to-date customer foundation that supports accurate reporting, targeted marketing, and a better overall customer experience.
Product recommendation solutions help guide customers and sales teams toward the most relevant products based on real purchasing behavior. Instead of relying on intuition, recommendations are driven by data: what customers bought in the past, which products are frequently purchased together, and how buying patterns evolve over time.
This approach delivers clear business value:
Improved customer satisfaction through relevant suggestions
Higher cross-sell and up-sell rates
Increased average basket size
Reduced sales cycle time for sales teams
Recommendations can be used across channels: at checkout, in digital platforms, or by sales representatives during customer interactions.
Recommendations are based on historical sales data and customer behavior. Different analytical methods can be applied depending on the use case and data maturity:
This method identifies products that are frequently bought together by analyzing past transactions. For example:
Tiles and glue appear together in 25% of all invoices (support).
Every tile purchase includes glue (confidence = 100%).
Half of glue buyers also purchase tiles.
These insights form the basis for cross-sell recommendations such as suggesting glue when tiles are added to the basket.

This approach looks at average customer behavior:
What products are usually bought together?
What did similar customers purchase?
Customers are then shown products that people “like them” often buy, making recommendations more relevant and easier to accept.
Predictive models estimate the likelihood that a customer will buy a specific product, given their previous purchases. This allows for more targeted recommendations and prioritization of products with the highest chance of conversion.
Suggest complementary products at checkout
Help sales representatives propose frequently paired items
Enable data-driven cross-selling based on actual buying behavior
The result is a dynamic recommendation table that lists relevant product combinations and their associated recommendations. This output updates automatically when new orders are placed or when the data is refreshed, ensuring recommendations remain current and accurate.

By grounding product recommendations in real transaction data, organizations can systematically increase revenue while making it easier for customers to find what they actually need.
Web personalization focuses on delivering a tailored user experience across digital platforms such as websites and portals. Instead of showing the same content to every visitor, users see information, recommendations, and messages that are relevant to their profile, behavior, and needs.
This enables:
More relevant content for each user
Targeted marketing campaigns
Up- and cross-selling opportunities
A clearer, more intuitive user experience
Many organizations struggle to personalize their digital platforms because:
Past user behavior is not tracked or stored
There is no user-level behavioral data
Technology to capture and activate this data is missing
There is no clear personalization strategy
As a result, all users see the same content, often leading to information overload and missed commercial opportunities.
Web personalization starts with building a Customer 360° view by collecting and unifying behavioral and profile data:
Tracking user behavior
The right tools and tracking mechanisms (such as cookies and event tracking) are installed to capture user interactions on the website.
Unifying data in a Customer Data Platform (CDP)
A CDP is used to store and combine real-time behavioral data with customer and profile information, creating a single, consistent view of each user.
Data activation
Based on this unified data, personalized content is pushed to specific users or segments. This includes content recommendations, targeted campaigns, and personalized page elements.

Consider a user logged into a digital platform. Based on their profile and past behavior:
Only relevant documents are shown on their dashboard
Irrelevant or overly complex information is hidden
Content adapts to their needs without overwhelming them
This ensures users quickly find what they need, while the platform remains focused and easy to navigate.

By implementing web personalization supported by a CDP, organizations move from static websites to dynamic digital experiences. Users receive relevant content, marketing becomes more effective, and digital channels become a direct driver of engagement and revenue.
Geo dashboarding supports B2B marketing and sales teams in identifying and prioritizing prospecting opportunities across different geographic regions. Instead of working with fragmented data or intuition, teams gain a clear visual overview of where potential customers are located and where sales efforts will have the most impact.
At NMBS, the B2B team is responsible for closing contracts with companies to provide train subscriptions for employees’ daily work commutes. However, several challenges limited their effectiveness:
Low data maturity: limited insight into current performance and market potential
Lack of internal alignment: no shared view on priorities or regional focus
Inefficient prospecting: no clear guidance on which companies to target
Without data insights or visual overviews, the B2B growth strategy felt like prospecting in the dark.
Geo dashboarding addresses these challenges by combining multiple data sources into one actionable view:
Internal sales and customer data
External data sources such as RSZ/ONSS
Geographic data on office and employee locations
An algorithm enriches and matches these datasets to identify potential B2B prospects and align them with ongoing sales efforts.
Using this approach:
Over 4 million employees were mapped to their office locations
The share of employees with a feasible train commute was calculated, based on whether train travel time is equal to or faster than driving
Current versus potential train commute adoption was calculated per company and per region
These insights are then visualized in an interactive geographic dashboard, showing:
Where NMBS already has strong penetration
Where untapped potential exists
Which regions and companies should be prioritized by sales team
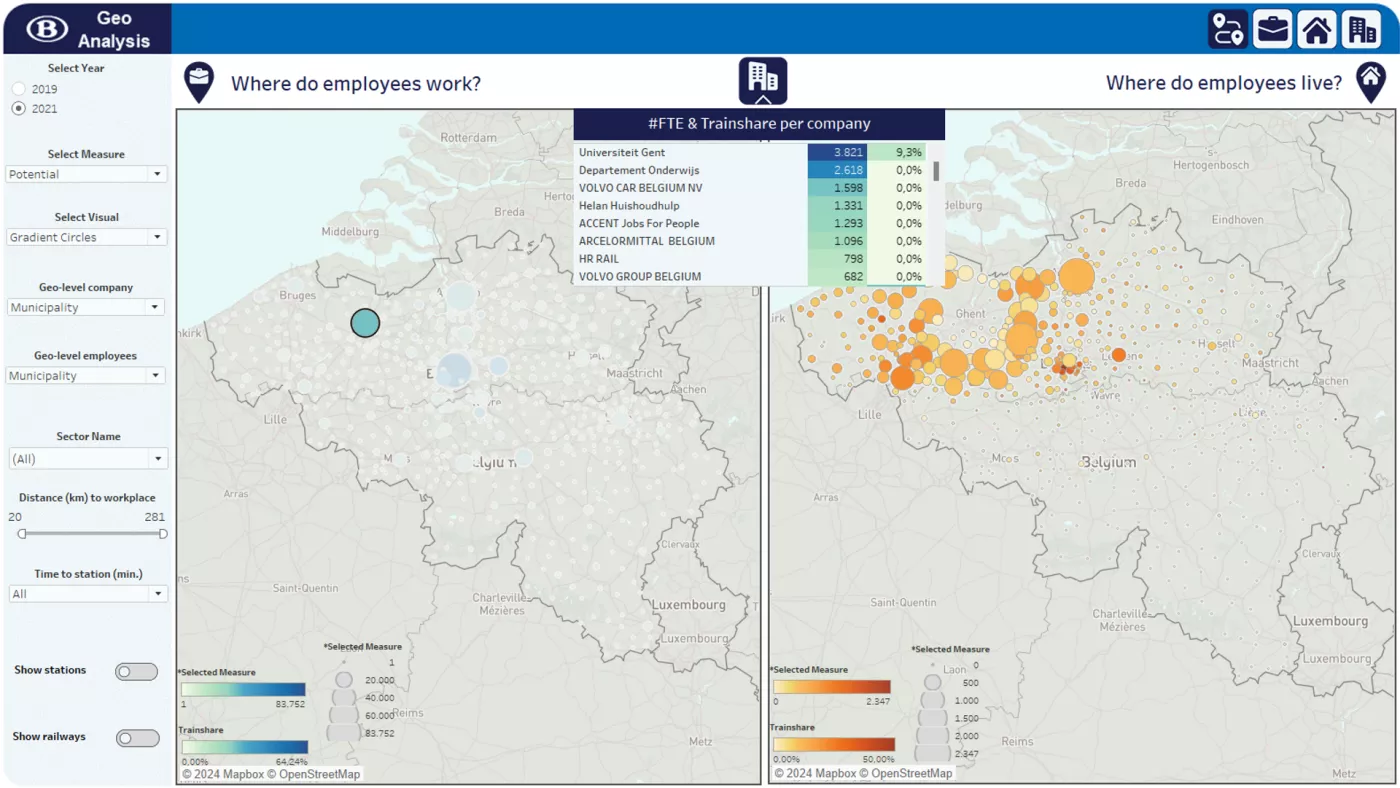
By visualizing prospecting opportunities geographically, B2B teams can focus their outreach on companies with the highest potential, align sales and marketing around the same insights, and move from reactive to targeted, data-driven prospecting.
For companies offering fixed-term leasing contracts, understanding whether customers will renew and when is critical. As contract end dates approach, uncertainty often remains about customer intentions. This makes it difficult to plan sales activities, allocate resources efficiently, and retain customers.
Without clear insight into renewal behavior, organizations face several challenges:
Missed renewal opportunities
Inefficient sales planning and misdirected dealer efforts
Higher customer churn
Unpredictable renewal revenue
As one finance manager put it:
“How can we predict which leasing customers will renew and when so dealers can contact the right customer at the right time?”
Contract renewal analytics address this challenge by using historical contract, customer, and behavior data to build a predictive model that estimates:
The likelihood that a customer will renew their contract
The expected timing of that renewal
This shifts the renewal process from reactive follow-ups to a proactive, structured approach.

The model outputs are directly usable by sales and service teams:
Dealers can prioritize customers with the highest renewal likelihood
Customers are contacted at the optimal moment, based on predicted timing
Sales resources are allocated more efficiently across the customer base
This data-driven approach delivers clear benefits:
Proactive customer engagement instead of last-minute outreach
More efficient use of sales and service capacity
Reduced customer churn
Better visibility into renewal behavior and customer lifecycle patterns

By transforming contract renewals into a strategic, insight-driven process, organizations improve both operational efficiency and long-term customer retention, while making renewal revenue more predictable.